DOHC2300 16V Engine and Auto Gearbox
Control Loom
Based on the DOHC2000 Engine, the 2.3 has similar control
functions, but with a new composite inlet manifold Ford claimed that it was
efficient enough without the Variable Resonance Inlet system that was fitted to
the 24V, hence the VIS valve control is deleted.
Note: Remember that in several locations the Scorpio uses very thin wires
which carry multiplex signals at 5V rather than more traditional 12V analogue
signals used in almost all other vehicles. This makes the wiring looms and
connectors much more susceptible to damage and is considered one of the
weaknesses of the cars now they are in the secondhand market.
Circuit Description
The electronic engine control system uses a network of sensors, switches, and
solenoids and the powertrain control module (PCM) (A147) to control fuel flow,
exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), ignition system functions, engine idle speed,
fuel evaporation to the atmosphere, transmission control and feedback functions
for emission-related components.
Voltage Supply
With the ignition off, voltage is present at pin 55 of the PCM (A147) to protect
the data stored in memory. With the ignition in run the DIS ignition coils (T4,
T5) and the fuel pump relay (K4) receive voltage. All other components of the
engine control system receive voltage from the fuel pump relay (K4). Pins 71 and
97 of the PCM (A147) also obtain voltage from the fuel pump relay (K4).
Ignition
With automatic transmission, the ignition system is controlled by the electronic
Distributorless Ignition System (DIS) module (A23). The electronic DIS module
(A23) controls the DIS ignition coils (T4, T5) and the crankshaft position
sensor (B43) and is connected to pins 23, 48, 49, and 50 of the PCM (A147). The
signal from pin 50 is used to detect intermittent ignition system faults. Pin 49
receives a Profile Ignition Pickup (PIP) value which is used by the PCM (A147)
to determine crankshaft position. The PCM (A147) also uses the PIP-Signal to
control gear shifting times (engine speed).
Fuel Pump
The fuel pump relay (K4) receives voltage from the ignition switch (N278) and is
controlled by pin 80 (pin 54 with passive anti-theft system (PATS)) of the PCM
(A147). Pin 40 of the PCM (A147) is used as a fuel pump monitor input. Current
flows to the inertia switch (N61) which shuts off the fuel pump in the fuel tank
unit (A31) in case of an accident. The fuel pump runs constantly during normal
operation, and the system pressure is preserved when the engine is shut off.
Transmission Control
The transmission hardware unit (A40) consists of the Transmission Speed Sensor
(TSS), the Transmission Oil Temperature (TOT) sensor and five solenoids. The PCM
(A147) provides outputs to the transmission through pins 1, 53, 54 (pins 72 and
80 with passive anti-theft system (PATS)) to control the shifting operations of
the transmission.
The stop lamp switch (N15) sends a "brake applied" signal to pin 92 of the PCM
(A147). This data is used to adjust the engine operations during deceleration.
Pins 10, 79 and 80 of the PCM (A147) lead to the instrument interface module
(A35).
Power Steering Pressure Switch
The power steering pressure switch (N96) sends a signal to pin 31 of the PCM
(A147) when the pressure is high. Under high power steering pressure, the PCM
(A147) increases the idle speed.
Engine Cooling Fan
The engine cooling fan relay (K45) and the engine cooling fan motors (M37, M38)
are controlled by pin 17 and 68 of the PCM (A147).
Instrument Cluster
The instrument cluster (A30) with integrated trip computer obtains a "fuel flow"
value from pin 43 of the PCM (A147) in order to calculate fuel economy and
distance-to-empty displays for the driver.
A/C Compressor Control
The A/C Wide Open Throttle (WOT) relay (K32) can be energised when pin 69 of the
PCM (A147) is connected to ground. This will cause the A/C compressor to be
disengaged, thus reducing engine load.
Voltage is applied to pin 41 of the PCM (A147) when the dual pressure switch
(N76) is closed. This information is used to determine engine load and to
control engine idle speed.
Octane Adjust
Pin 30 of the PCM (A147) measures the voltage drop across the octane adjust plug
(D2) and uses this information to modify ignition spark advance.
Diagnostic and Ground Connections
Pins 13, 15 and 16 of the PCM (A147) lead to the Data Link Connector (DLC)
(D20).
Pins 24, 51, 77 and 103 of the PCM (A147) are connected to ground G10.
Pin 25 of the PCM (A147) is connected to ground G7.
Solenoids
The fuel injectors (Y108, Y109, Y110, Y111) obtain their voltage from the fuel
pump relay (K4). The PCM (A147) (pins 75, 101, 74 and 100 or pins 70, 96, 20 and
95 with passive anti-theft system (PATS)) controls the four fuel injectors
continuously and individually. The injection quantity, that is, the duration of
the input signal, is determined by the temperature, load and rpm of the engine
as well as by the composition of the exhaust gases. The longer the pulse, the
greater the amount of fuel that passes through the injector.
The idle speed control valve (Y13) obtains its distribution voltage from the
fuel pump relay (K4). The PCM (A147) compares the stored desired engine idle
speed value with the actual engine idle speed and regulates the idle speed
control valve (Y13) from pin 83. The idle speed control valve (Y13) varies the
air volume into the engine via an auxiliary air passage.
The canister purge solenoid valve (Y1) is needed to open and close the activated
carbon canister. When the valve is energised by connecting pin 56 of the PCM
(A147) to ground, the fuel vapours from the fuel tank can be drawn into the
engine, mixed with the intake air and burned.
The Electr. Vacuum Regulator (EVR) solenoid valve (Y33) allows a measured
quantity of exhaust gas to be directed back into the intake manifold. The
exhaust gas introduced into the intake manifold dilutes the incoming mixture and
reduces peak gas temperatures, thus reducing NOx emissions. The valve is
controlled by pin 47 of the PCM (A147). The EGR system does not operate
during conditions of over-run or wide open throttle.
Sensors
Pin 91 of the PCM (A147) serves as ground for the Exhaust Pressure Transducer
(EPT) sensor (B40), the Barometric Air Pressure (BAP) sensor (B70), the Throttle
Position Sensor (TPS) (B8), the heated oxygen sensors (HO2S) (B89, B90), the
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor (B10), the Air Charge Temperature (ACT)
sensor (B5), the transmission range sensor (B120), the oil temperature sensor of
the transmission hardware unit (A40), the power steering pressure switch (N96)
and the octane adjust plug (D2).
The Exhaust Pressure Transducer (EPT) sensor (B40), the Barometric Air Pressure
(BAP) sensor (B70) and the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) (B8) all receive a
reference voltage of 5 V from pin 90 of the PCM (A147).
The Exhaust Pressure Transducer (EPT) sensor (B40) measures the pressure
difference in the feed exhaust and sends its signal to pin 65 of the PCM (A147).
The sensor is part of the EGR system.
The Barometric Air Pressure (BAP) sensor (B70) measures barometric pressure and
sends its signal information to pin 34 of the PCM (A147). This information is
used to help calculate fuel delivery.
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) (B8) consists of a potentiometer mounted on
the throttle blade shaft that sends its signal to pin 89 of the PCM (A147).
Using this signal, the module can compute the position of the throttle valve
(idle, partial load, or wide open) and use the input to help calculate fuel
delivery.
The pre-catalyst heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) (B89) measures the amount of oxygen
in the exhaust gases. Bounce signals are sent from the pre-catalyst heated
oxygen sensor (HO2S) (B89) to pin 60 of the PCM (A147). This measurement is made
so that the PCM (A147) can maintain the air/fuel mixture composition close to
the value of Lambda=1 for correct operation of the catalytic converter. Since
the sensor does not function until it has reached its operating temperature, it
contains a heating element to speed warm-up time.
The post-catalyst heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) (B90) is installed behind the
catalytic converter and sends bounce signals to pin 35 of the PCM (A147) to
ensure correct operation of the pre-catalyst heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) (B89).
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor (B10) (a temperature-dependent
resistor) receives its input voltage from pin 38 of the PCM (A147). The sensor
provides the PCM (A147) with the engine operating temperature needed to help
calculate fuel delivery.
The Air Charge Temperature (ACT) sensor (B5) provides the PCM (A147) pin 39 with
a signal proportional to the temperature of the incoming air charge. The data is
used to help calculate fuel delivery.
The transmission range sensor (B120) sends a start input signal to pin 64 of the
PCM (A147). The PCM (A147) will not allow the engine to start unless the
transmission is in park (P) position.
The Transmission Oil Temperature (TOT) sensor of the transmission hardware unit
(A40) sends its signal to pin 37 of the PCM (A147).
The Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) (B11) sends a square wave signal, whose frequency
is proportional to the vehicle road speed, to pin 58 of the PCM (A147).
The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor (B22) measures the quantity of air passing into
the engine via the air filter. The information is then fed back to the PCM
(A147), pins 36 and 88, and is used to help calculate fuel delivery.
The crankshaft position sensor (B43) provides the electronic DIS module (A23),
pins 5 and 6, with the position of the crankshaft. This data is used for correct
timing of the injectors at engine start-up.
The Transmission Speed Sensor (TSS) of the transmission hardware unit (A40)
provides the PCM (A147), pin 84, with the transmission shaft speed. The data is
used to control the shifting sequence for the transmission.
The camshaft position sensor (B41) provides the PCM (A147), pin 76, with a
reference point for the number 1 cylinder, which is necessary to ensure the
correct sequence of injector opening.
Connections
The Powertrain Control Module is shown as C401 instead of
C402 shown on the introduction page, but the two are identical.

Note C112 is next to C110 on the offside bulkhead and the
pin configurations are identical.
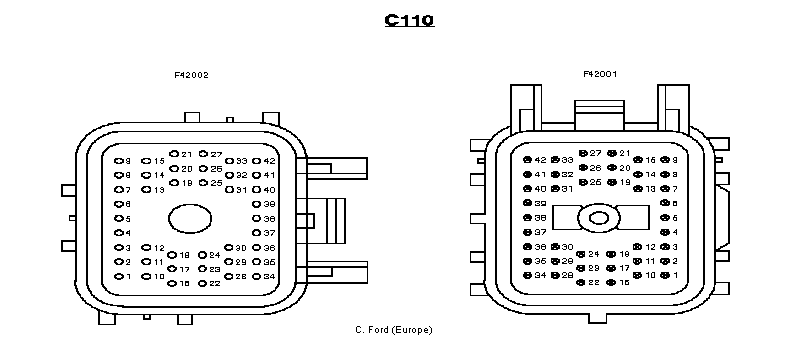
Now a view of the connectors on the 2.3 engine - manual
shown, but auto connections are the same.

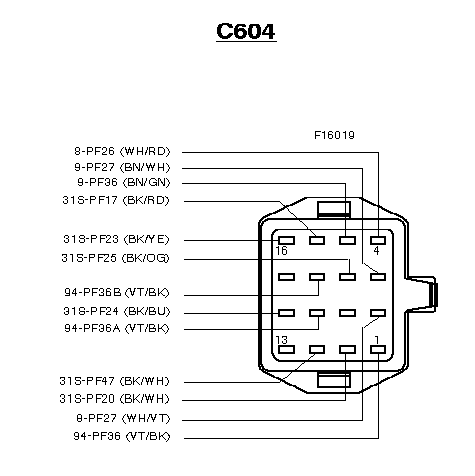
Engine Loom Connections
Note: The first 4 connections commence not from the PCM
but from the EDIS module C766 on the offside bulkhead beside the headlamp.


