.V6 12V Engine and
Autobox Control Loom
The 12V Cologne engine is an interesting case study. It
uses a hybrid A4LDe gearbox carried over from the Ford Granada, in which the
older EEClV powertrain control module (PCM) controls only the 3/4 gear shift
and the O/D (4th) gear solenoids. This is to enable the PCM to slur the
gearchanges by slightly retarding the ignition during changes.
Note: the 12V does not have OBD2 compatible systems and
cannot be read using the OBD2 lead and software used on other Scorpios. The
EEC-IV can however be read and reset using a STAR tester.
First - compatibility. Yes, the Granada 12V auto is the
same as the Scorpio - but only those built after February 1995 have the same
wiring to the sensors. An earlier Granada engine will physically fit perfectly,
but the electrical connectors are wired differently. The IACV and 1, 2 and 3
Injectors have different pinouts on the PCM. Also note that this is the build
date of February 1995, not the date of first registration.
Circuit Description
The electronic engine control system uses a network of sensors, switches, and
solenoids and the PCM (A147) to control fuel flow, ignition system functions,
engine idle speed, fuel evaporation to the atmosphere and transmission control.
Voltage Supply
With the ignition off, voltage is present at pin 1 of the PCM (A147) to protect
the data stored in memory. With the ignition in run the ignition coil (T1), the
TFI IV ignition module (A1), the fuel pump relay (K4), the kickdown relay (K10)
and the kickdown switch (N2) receive voltage. All other components of the engine
control system receive voltage either from the PCM (A147) or from the fuel pump
relay (K4).
Ignition
After the engine has been started, the input signals from the TFI IV ignition
module (A1) are sent to the PCM (A147) to be evaluated. Pin 36 of the PCM (A147)
controls the ignition voltage by sending a SPOUT-Signal (Spark-Out-Signal) to
the TFI IV ignition module (A1).
Fuel Pump
The fuel pump relay (K4) is controlled by pin 22 of the PCM (A147). Current
flows to the inertia switch (N61) which shuts off the fuel pump in the fuel tank
unit (A31) in case of an accident. The fuel pump runs constantly during normal
operation, and the system pressure is preserved when the engine is shut off.
Kickdown Control
When the kickdown switch (N2) is activated in vehicles with automatic
transmission, the automatic transmission shifts down to a lower gear when below
a certain rpm and in gear lever position D, in order to have enough power
reserve for overtaking.
Stop Lamp Switch
The stop lamp switch (N15) sends a "brake applied" signal to pin 18 of the PCM
(A147). This data is used to adjust the engine operations during deceleration.
Engine Cooling Fan
The engine cooling fan relay (K45) and the engine cooling fan motors (M37, M38)
are controlled by the engine cooling fan temperature switch (N169).
Instrument Cluster
The instrument cluster (A30) with integrated trip computer obtains a "fuel flow"
value from pin 34 of the PCM (A147) in order to calculate fuel economy and
distance-to-empty displays for the driver.
A/C Compressor Control
The A/C Wide Open Throttle (WOT) relay (K32) can be energised when pin 54 of the
PCM (A147) is connected to ground. This will cause the A/C compressor to be
disengaged, thus reducing engine load.
Voltage is applied to pin 10 of the PCM (A147) when the dual pressure switch
(N76) is in neutral position. This information is used to determine engine load
and to control engine idle speed.
Octane Adjust
Pins 23 and 28 of the PCM (A147) measure the voltage drop across the octane
adjust plug (D2) and uses this information to modify ignition spark advance.
Diagnostic and Ground Connections
Pins 17 and 48 of the PCM (A147) lead to the Data Link Connector (DLC) (D20).
Pins 40 and 60 of the PCM (A147) are connected to ground G10.
Pin 20 of the PCM (A147) is connected to ground G7.
Solenoids
The fuel injectors (Y108, Y109, Y110, Y111, Y112, Y113) obtain their voltage
from the fuel pump relay (K4). Pins 58 and 59 of the PCM (A147) control the six
fuel injectors. The injection quantity, that is, the duration of the input
signal, is determined by the temperature, load and rpm of the engine as well as
by the composition of the exhaust gases. The longer the pulse, the greater the
amount of fuel that passes through the injector.
The idle speed control valve (Y13) obtains its distribution voltage from the
fuel pump relay (K4). The PCM (A147) compares the stored desired engine idle
speed value with the actual engine idle speed and regulates the idle speed
control valve (Y13) from pin 21. The idle speed control valve (Y13) varies the
air volume into the engine via an auxiliary air passage.
The canister purge solenoid valve (Y1) is needed to open and close the activated
carbon canister. When the valve is energised by connecting pin 31 of the PCM
(A147) to ground, the fuel vapours from the fuel tank can be drawn into the
engine, mixed with the intake air and burned.
Sensors
Pins 46 and 49 of the PCM (A147) serve as ground for the Manifold Air Pressure
(MAP) sensor (B2), the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) (B8), the heated oxygen
sensors (HO2S) (B47, B48), the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor (B10) and
the Air Charge Temperature (ACT) sensor (B5).
The Manifold Air Pressure (MAP) sensor (B2) and the Throttle Position Sensor
(TPS) (B8) both receive a reference voltage of 5 V from pin 26 of the PCM
(A147).
The Manifold Air Pressure (MAP) sensor (B2) is a pressure-sensitive device which
delivers electronic signals to pin 45 of the PCM (A147). The frequency of the
output signal changes with the intake manifold pressure. The PCM (A147) uses
this signal to adjust the air/fuel mixture and the ignition timing based on the
current engine operating conditions.
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) (B8) consists of a potentiometer mounted on
the throttle blade shaft that sends its signal to pin 47 of the PCM (A147).
Using this signal, the module can compute the position of the throttle valve
(idle, partial load, or wide open) and use the input to help calculate fuel
delivery.
The pre-catalyst heated oxygen sensors (HO2S) (B47, B48) measure the amount of
oxygen in the exhaust gases. Bounce signals are sent from the pre-catalyst
heated oxygen sensor RH (HO2S) (B48) to pin 29 of the PCM (A147) and from the
pre-catalyst heated oxygen sensor LH (HO2S) (B47) to pin 43 of the PCM (A147).
This measurement is made so that the PCM (A147) can maintain the air/fuel
mixture composition close to the value of Lambda=1 for correct operation of the
catalytic converter. Since the sensors do not function until they have reached
their operating temperature, they contain heating elements to speed warm-up
time.
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor (B10) (a temperature-dependent
resistor) receives its input voltage from pin 7 of the PCM (A147). The sensor
provides the PCM (A147) with the engine operating temperature needed to help
calculate fuel delivery.
The Air Charge Temperature (ACT) sensor (B5) provides the PCM (A147), pin 25,
with a signal proportional to the temperature of the incoming air charge. The
data is used to help calculate fuel delivery.
The transmission range sensor (B120) sends a start input signal to pin 30 of the
PCM (A147). The PCM (A147) will not allow the engine to start unless the
transmission is in park (P) position.
The Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) (B11) sends a square wave signal, whose frequency
is proportional to the vehicle road speed, to pin 3 of the PCM (A147). Together
with other data received by the PCM (A147), vehicle speed is used for idle speed
control, fuel enrichment during acceleration and fuel cut-off during
deceleration.
Connectors
The electronics being different, we must look at the
connectors first. The PCM is still behind the glovebox under the dash, but the
multiplug is C2503.

It has 60 pins rather than the 104 of the EECV.
The engine loom connector is a single multiplug C2513,
physically identical to the C110 and C112 in other Scorpios.

I know it seems obvious, but it is easy to forget that
when the connector is separated and both faces are upward, they are mirror
images of each other. 9 on the top left connects with pin 9 on the top right.
The 12V uses the TFI IV Ignition module. Many connections
are made to this direct from the PCM, so a view of the connector would be
useful. Unfortunately, numbering the pins was not in general usage during the
inherited Granada production, so the colour codes must suffice.

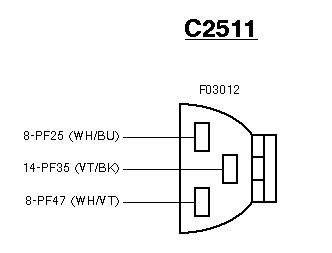
As you would expect, compared with the EECV the gearbox
connector C2511 is much simpler:
Now an engine view so that we can place these connectors.
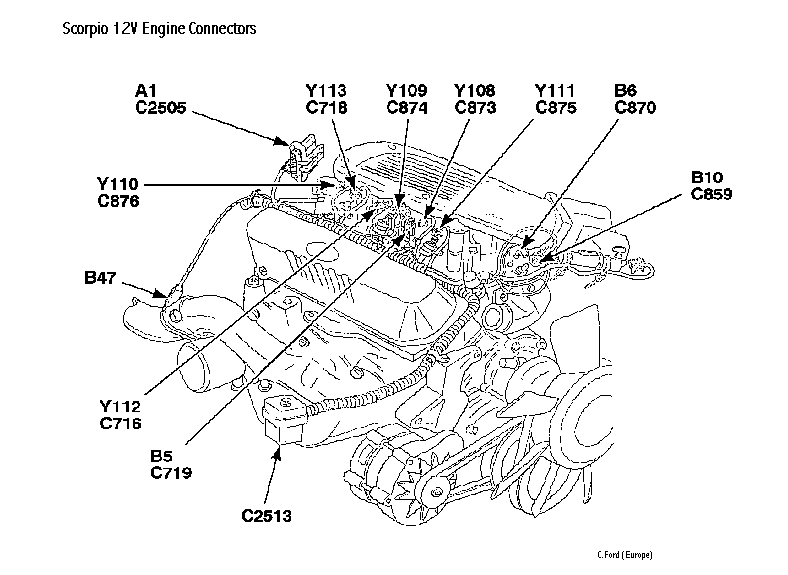
Yes, I know that the drive belts are the Granada
arrangement, but this is the view that is given.
Now for the detail. The engine loom travels from the PCM
through a grommet in the bulkhead and runs round to the LH engine bay and the
connector C2513. The top half of the connector contain the pins and the engine
loom which runs through the V of the cylinder heads and down the bell housing of
the automatic gearbox, called the Transmission Hardware Unit (HTU) In most cases
there is a direct unbroken connection between the PCM connector C2503 to the
bulkhead multiplug C2513. From this there is a direct link to each of the pins
in the connectors mounted on the engine and gearbox. By checking these pins with
a multimeter for continuity, resistance and insulation it is possible to track
down any faults in the loom.
Now are you sitting comfortably? Then we'll begin.
Engine Control Connections thru C2513

